Copyright©2004 by Daniel B. Sedory
If you've never heard of Borland before, I suggest you spend a little time reading about their C++ 5.5 software here:
![]() http://www.borland.com/bcppbuilder/freecompiler/
.
http://www.borland.com/bcppbuilder/freecompiler/
.
If you want to
get right into the programs, here are the direct links to the
compiler/linker tools archive downloads:
freecommandLinetools.exe
(8.7 MiB; 8/24/2000) and their
TurboDebugger.exe
for Windows (TD32;
590 KiB; 6/6/2000).
Some of the programs/files included in the archives are:
A Windows Help file (bcb5tool.hlp) is also included that will give you detailed information about these programs.
Although you may wish to read the "Supplementary
Information" page at Borland, do not
use the path found in the configuration instructions there! We'll be
using C:\bc55\ (instead of
"C:\BORLAND\BCC55\") so we can have shorter command
lines (and because it makes navigating in a Command window much easier).
So, to configure your system, use the following instead:
|
NOTE: You must add two configuration files into your C:\bc55\bin directory, bcc32.cfg and ilink32.cfg. The format of each file is plain text containing the following lines:
You can download
both files together here: bc55cfg.zip
. If you do not install the Borland C++ 5.5 files into C:\bc55, then you'll also have to edit the location of the \bin folder in each of the .cmd Batch programs I've created for you in these lessons! We must also add the location of our new C++ 5.5's \bin folder to the PATH statement of the OS's permanent Environment variables! (If you didn't, you'd have to ENTER: path=C:\bc55\bin each time you used the compiler or any of its tools!) To do this under Windows™2000/XP, proceed as follows:
2. In the window that pops up, click on the "Advanced" tab. 3. Click on "Environment Variables..." (the middle button). 4. Under "System Variables" (the bottom box) look for and then click on (highlight) the Variable, "Path" like this: 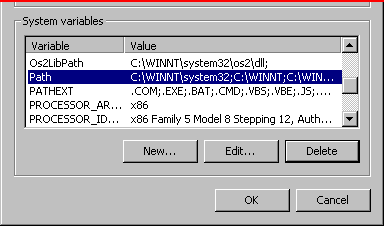
5. Click on the "Edit..." button, and something like this will pop up: 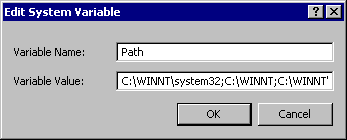 There are usually
many pathways in the "Variable Value" box; and at least these:
C:\WINNT\system32;C:\WINNT;C:\WINNT\System32\Wbem
|
In the context of programming (not hard drives), IDE is an abbreviation for Integrated Development Environment; which is a graphical interface (or "front end") for the command-line compilers and linkers that are the backbone of all C, C++ and various other programming language distributions. The main function of an IDE is to keep your focus on the lines of code you're writing by making the compiling, linking and even the handling of error/warning messages as easy as clicking on a toolbar button or pressing a function key!
The major drawback of the free Borland package has been the fact that it does not include an IDE. To obtain one, you'd normally have to buy theirs or someone else's product! There have been a number of free source file editors available, but editors that simply highlight keywords or even try to launch a few programs are no substitute for a true IDE. However, we did finally find an editor called SciTE (Scintilla Text Editor) which not only has the capability of launching the compiler and linker with parameters, but will show all error messages in the window and jump to each line in the source code when you click on the displayed errors!
You can either get SciTE right now (by selecting a download site near you from this link: Sc1.exe and saving the single executable file in your C:\bc55\bin folder), or wait until we explain how to use it in a separate lesson. We'll be compiling a few examples using some .CMD Batch programs first.
 Back
to The Starman's Realm Index page!
Back
to The Starman's Realm Index page!